The Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) is a term that can send shivers down the spine of any Windows user. This critical failure, officially known as a Stop Error, signals a significant issue within the system—be it due to hardware failures, driver conflicts, or corrupted system files.
The immediate and unwelcome appearance of a blue screen can not only disrupt your work but also poses a risk of data loss and system damage if not addressed promptly.
This guide aims to demystify the BSOD, providing insights into its causes, diagnostics, and solutions to restore your system to good health.
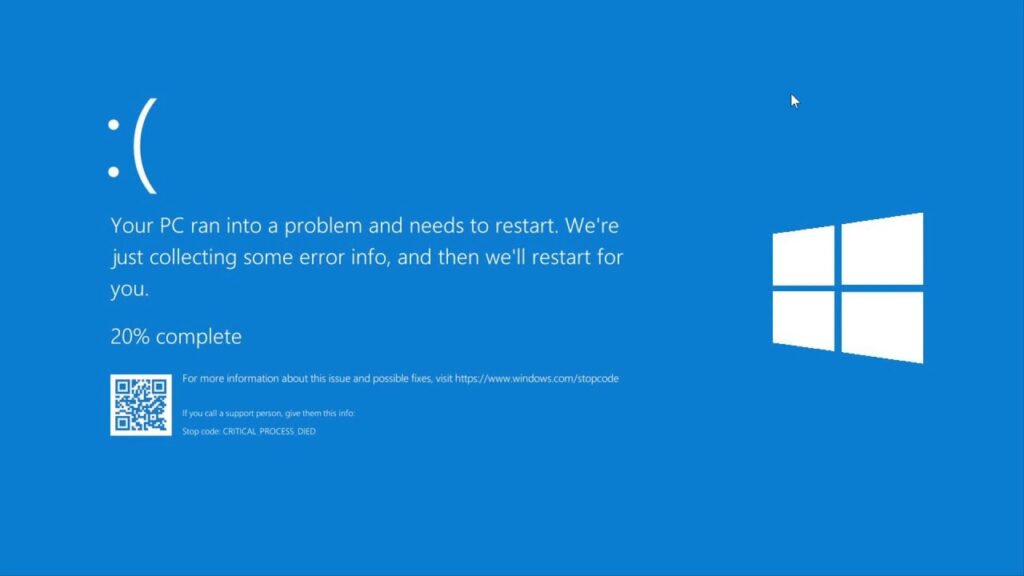
Understanding BSOD
At its core, the BSOD is a protective measure by the Windows operating system. It halts the system to prevent further damage or data loss after detecting a critical error. Common triggers include hardware malfunctions, incompatible drivers, and corrupt system files. Recognizing the root cause is essential for effective troubleshooting.
Common BSOD Error Codes
Error codes such as IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL, PAGE_FAULT_IN_NONPAGED_AREA, and SYSTEM_SERVICE_EXCEPTION are among the many that can appear on the BSOD. Each code offers clues to the underlying issue, guiding the troubleshooting process. Documenting these codes before proceeding with fixes is crucial.
Diagnosing the Problem
The first step in addressing a BSOD is to note the error code and any accompanying messages. Windows’ Event Viewer can be a valuable tool in this phase, offering a log of system events leading up to the crash. Additionally, Windows comes equipped with diagnostic tools that can help pinpoint hardware or software issues contributing to BSOD incidents.
Solutions to Fix BSOD
Hardware-Related Fixes
- Overheating Components: Ensure your PC’s ventilation is not obstructed and consider cleaning dust from fans and heatsinks.
- Component Testing: Use Windows Memory Diagnostic and hard drive checks to test for failing hardware.
- Driver Updates: Conflicts between hardware and drivers can often be resolved by updating or rolling back to previous driver versions through Device Manager.
Software-Related Fixes
- Safe Mode: Booting into Safe Mode can help you troubleshoot by running Windows with a minimal set of drivers and services.
- System Restore: Reverting to a system restore point before the issues began can resolve BSOD errors caused by recent software changes.
- Windows Update: Keeping your system updated ensures that you have the latest security patches and system improvements.
- SFC and DISM: The System File Checker and Deployment Image Servicing and Management tools can repair or replace corrupted system files.
Preventing Future BSODs
To fortify your Windows PC against the dreaded Blue Screen of Death (BSOD), adopting a proactive approach towards system maintenance and management is essential. Ensuring your system operates smoothly requires regular checks and updates, which can significantly mitigate the risk of encountering BSODs.
First and foremost, keeping your operating system and drivers up to date is critical. Manufacturers often release updates that fix known bugs and compatibility issues that could lead to BSODs. Use the Windows Update feature to automatically download and install the latest updates for your system. Similarly, checking for the latest drivers for your hardware components can prevent conflicts that may cause system crashes.
Routine system health checks play a pivotal role in maintaining your PC’s integrity. Regular disk cleanup and defragmentation help optimize your storage space and improve system performance, reducing the likelihood of software conflicts that could trigger a BSOD. Tools built into Windows, like the Disk Cleanup utility and the Optimize Drives feature, make these tasks straightforward and user-friendly.
Moreover, the internet is rife with threats that can compromise your system’s stability. Employing a robust antivirus solution and exercising caution when downloading software or opening email attachments can shield your PC from malicious software. Untrusted or pirated software not only poses a security risk but can also introduce system errors leading to BSODs.
By integrating these preventative measures into your regular computing routine, you can significantly lower the chances of experiencing BSODs, ensuring a more stable and reliable Windows experience.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many BSOD issues can be resolved with the steps outlined above, certain problems may require a professional’s touch, especially when dealing with complex hardware failures or deeply rooted software issues. If your troubleshooting efforts do not resolve the problem, or if you’re uncomfortable performing any of the recommended steps, seeking assistance from a certified technician is advisable.
Conclusion
The Blue Screen of Death, while daunting, is not the end of the line for your Windows PC. With a methodical approach to diagnosing and addressing the underlying causes, most BSOD issues can be resolved. Armed with the knowledge and tools provided in this guide, you can tackle BSOD errors with confidence, ensuring your system’s longevity and reliability.
Remember, the key to minimizing BSOD occurrences lies in regular system maintenance, cautious updating, and vigilant protection against malware. By adopting these best practices, you can maintain a stable and healthy Windows environment, significantly reducing the likelihood of future blue screen interruptions.

